The shift from conscious effort to automaticity. We dissect the “chunking” mechanism of the basal ganglia and the procedural protocols to install, stack, and cement new behavioral loops.
The Evolutionary Design
Your brain is an energy hog. It burns massive amounts of fuel just to think. To survive, nature built a way to save that energy. The brain automates repetitive actions. It turns complex behaviors into automatic scripts. This preserves your mental resources for sudden threats or new problems. You do not think about tying your shoes. You just do it. This automation allowed early humans to focus on hunting and staying alive.
The Modern Analogy
Habit formation is like tracing the same line in a notebook so many times that it leaves a permanent groove in the page. At first, the pencil mark is light. You must focus to keep your hand steady. But you repeat the motion. You trace it again and again. Eventually, the pressure creates a deep channel in the paper. The pen tip falls into this groove on its own. It slides down the path without your effort. This is dangerous if the path is bad. You become stuck in the rut you created.
The Upgrade Protocol
You cannot simply erase a deep groove. The impression on the page is already there. To fix this, you must carve a new line. You pick a fresh spot on the paper. You press the pen down with intention. The first few strokes are difficult. The pen wants to slip back into the old, deep channel. You must resist that pull. Keep tracing the new path. Do it every day. Soon, the new groove becomes deep and smooth. The old path fills with dust and fades away.








NEUROBIOLOGICAL CONTEXT
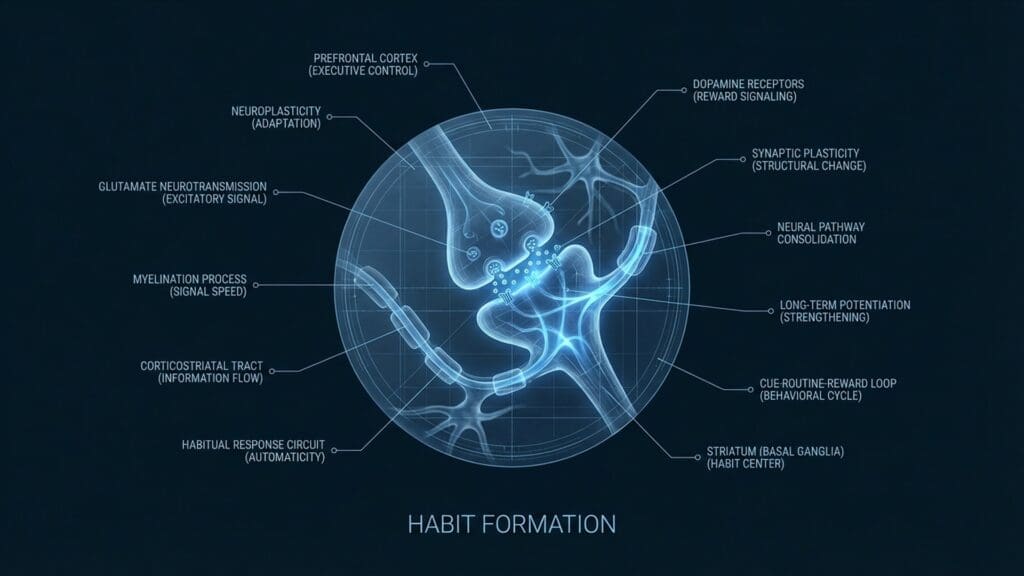
Habits are the brain’s attempt to conserve metabolic energy. When you first perform a novel action, the Prefrontal Cortex (PFC) is highly active, managing every step. As the behavior is repeated, this activity shifts to the Basal Ganglia, an ancient structure deep in the brain responsible for procedural memory. This process is called “Chunking”: the brain converts a complex sequence of actions into a single automatic unit. Once chunked, the behavior requires zero conscious effort to execute.
Every habit relies on a three-part neurological loop encoded in the striatum:
The Cue: A trigger (time, location, or emotional state) that signals the basal ganglia to engage automatic mode.
The Routine: The physical or mental action itself.
The Reward: The release of dopamine that tells the brain “this loop is worth remembering” for next time. To build a habit, you must make the cue obvious; to break one, you must disrupt the cue or replace the routine while keeping the reward.
The hardest part of habit formation is “Limbic Friction”—the activation energy required to overcome the body’s resting state.
Task Bracketing: The most effective protocol is to anchor a new habit to a specific biological state change (like immediately after waking up or right after a workout). This utilizes the existing dopamine momentum to reduce the neurological friction of starting.
Procedural Memory: It takes repetitions, not just time, to move a behavior from the “declarative” memory (knowing how to do it) to “procedural” memory (doing it without thinking).
Join my inner circle for exclusive insights and breakthroughs to elevate your life.
Limited Availability
Your Journey to Unparalleled Personal and Professional Growth Starts Here
Limited Availability
A Truly Bespoke, One-on-One Journey with Dr. Sydney Ceruto
Download The Influence Within and discover how small shifts lead to big transformations.